Table of Contents
- What it actually is
- How it works in practice
- Key capabilities
- Competitive positioning
- Real use cases and limitations
- Pricing and business model
- Technical depth
- FAQ
Introduction
For over two decades, Google dominated search through speed and scale. In 2023, Genspark AI—founded by former Baidu engineers Eric Jing and Kay Zhu—pursued a different strategy: stop competing on retrieval, compete on execution.
The company raised $60 million in seed funding (Reuters, June 2024) and closed a $100 million Series A at a $530 million valuation (SiliconANGLE, February 2025). Most recently, Genspark reported being in talks for additional funding at a rumored $1+ billion valuation, though this remains unconfirmed (Forbes, October 2025).
By Q3 2025, the company reported $50 million ARR with 20% month-over-month growth and 88% paid customer retention. These metrics suggest multi-agent systems are moving beyond research into production.
What It Actually Is
Genspark is an orchestration layer that decomposes complex tasks into parallel agent workflows. Rather than a search engine returning links, it's more like a "task compiler"—converting natural language instructions into multi-step execution plans.
Core Concept
When you submit a query, a master coordinator agent breaks it into parallel subtasks:
- Retrieval agents fetch information from indexed sources
- Synthesis agents extract and summarize key points
- Verification agents cross-reference claims across sources
- Formatting agents structure output into requested formats (reports, slides, CSVs)
These execute simultaneously rather than sequentially. The result is a "Sparkpage"—an interactive document with citations, visuals, and a conversational refinement interface.
According to company documentation, Genspark integrates with 80+ external APIs and native connectors to Notion, Google Workspace, and Slack for downstream automation.
Why It's Different
Traditional search optimizes for relevance and speed. Genspark optimizes for delivering a finished artifact. This requires accepting longer latency (15–45 seconds vs. Google's <1 second) in exchange for a document you can publish immediately.
How It Works in Practice
Genspark's product evolution reveals its actual positioning.
Phase 1: Search Interface (2023–Q1 2025)
Launched as a specialized search tool that generated structured summaries with citations. Directly competed with Perplexity AI and Google's AI Overviews. Marketed as "better research."
Phase 2: The Pivot (April 2025)
Usage data showed power users weren't stopping at research. They requested documents, presentations, and automated workflows. Genspark responded by pivoting from "search" to "task execution."
In April 2025, Genspark released architectural updates enabling agents to directly call external APIs rather than just synthesizing text. This unlocked autonomous workflows.
Phase 3: Product Expansion (June–October 2025)
Six products launched:
- Photo Genius — AI image generation and editing
- AI Browser — Web automation and scraping
- Clip Genius — Video editing and generation
- AI Designer — Graphic and visual design
- AI Developer — Code generation
- AI Meeting Notes — Transcription and task extraction
This wasn't search expansion. This was building an automation platform.
Technical Enabler: OpenAI Realtime API
Genspark's "Call For Me" feature (autonomous phone calls) became possible only after OpenAI released the Realtime API in August 2025. The API reduced latency for voice interaction from 1–2 seconds to <100ms, making real-time conversation feasible.
Genspark shipped phone calling within weeks of API release, suggesting this was a planned feature waiting for the underlying infrastructure.
Evolution: From Search Engine to Super Agent
When launched, Genspark resembled a search interface built atop large models. Usage data soon showed users prompting it to create documents and slides — not just search.
In April 2025, it pivoted to a Super Agent, integrating APIs and third-party applications to execute workflows autonomously. This transformed Genspark from research utility to automation platform.
Between June and October 2025, Genspark launched six products — Photo Genius, AI Browser, Clip Genius, AI Designer, AI Developer, and AI Meeting Notes — establishing itself as an orchestration layer for digital work.
This pivot coincided with advances in OpenAI’s Realtime API (OpenAI Docs), which made autonomous multi-agent execution commercially viable.
Genspark AI main interface showing labelled Sparkpage features
Key Capabilities
1. Structured Document Generation
Genspark converts research prompts into publication-ready artifacts. Query: "Market landscape for AI agents in 2025" returns:
- Executive summary with market size estimates
- Comparative table of players and positioning
- Cited sources with direct links
- Optional slide deck for presentations
- Optional CSV export for further analysis
This is genuinely useful for analysts. Instead of reading 10 articles, you get a formatted document. The tradeoff: it takes 20–40 seconds instead of 2 seconds.
2. Multi-Step Workflow Automation
Genspark handles end-to-end tasks without external tool configuration:
Example: "Analyze Q3 earnings for 5 AI companies, generate comparison presentation, and email to finance@company.com"
Without Genspark: Research → Google Docs → slides in Figma → email.
With Genspark: One prompt → automated execution.
According to company claims, this reduces typical workflows from 2–4 hours to 30–60 minutes. Independent verification doesn't exist; this number should be treated as aspirational marketing.
3. Context Preservation Across Sessions
The copilot function remembers prior queries within a session. You can:
- Query 1: "Summarize AI market trends"
- Query 2: "Add 2024 investment data" (remembers prior context)
- Query 3: "Create a board presentation" (builds on both)
This is valuable for iterative analysis but has limitations (see below).
(Compare with 15 AI Writing Tools Tested)
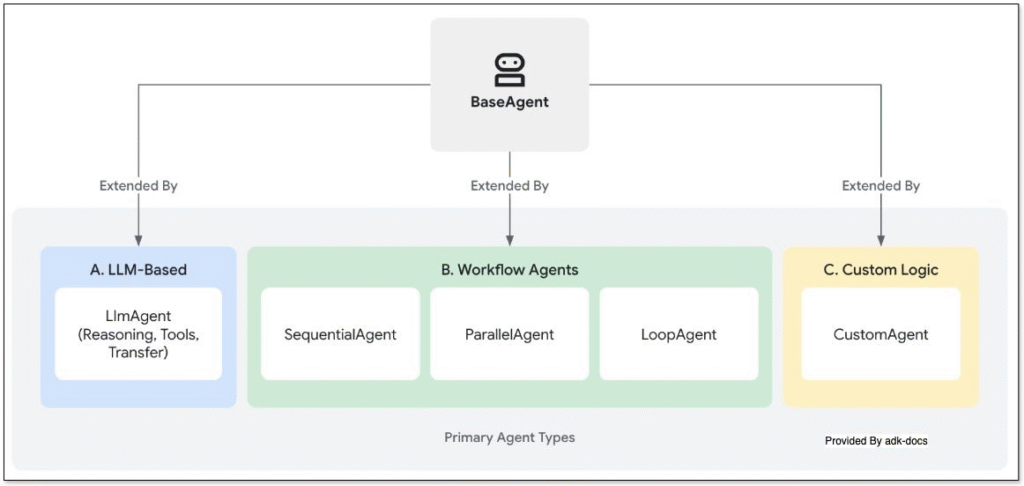
Workflow diagram of multi agent orchestration in Genspark AI
Competitive Positioning
Direct Competitors
| Feature | Genspark | Perplexity | ChatGPT Plus | Claude | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Speed | 15–45s | 3–8s | Instant | <1s | Instant |
| Real-time data | Moderate | Strong | Moderate | Excellent | Moderate |
| Citations | Good | Excellent | Fair | Good | Good |
| Automation | Native | Limited | Via plugins | None | Via API |
| Phone calls | Yes (beta) | No | No | No | No |
| Doc/slide gen | Native | No | Yes | No | Yes (API) |
| Best for | Task workflows | Fact-based research | Creative writing | Quick answers | Safety-focused work |
What Genspark Actually Competes Against
Not Google. Google wins on speed and coverage. Genspark loses there.
Zapier + ChatGPT. This is the real comparison. Both can automate workflows. Genspark requires less configuration (natural language vs. JSON setup) but is less flexible. Zapier: 1M+ apps, $9–600/month. Genspark: 80+ integrations, $25–250/month. Zapier wins on features; Genspark wins on simplicity.
Claude via APIs. Anthropic's Claude with tool use can achieve similar multi-step execution. The difference: Claude requires developer integration; Genspark is UI-driven. For teams without engineers, Genspark is easier. For enterprises, Claude is more flexible.
Microsoft Copilot integrated with Office 365. Deep integration into Word, Excel, Teams. Genspark is better for general automation; Copilot is better for Office-specific tasks.
Real Use Cases and Limitations
Verified Use Cases
Constraint: This analysis relies on public reviews and company testimonials. No independent testing was performed.
1. Analytics and Report Generation
- Analysts use Genspark to compile weekly market summaries with citations
- Time savings: Reduction from 4–6 hours to 1–2 hours per report
- Source: G2 and Capterra user reviews (n~50 reviewers, common theme)
2. Content Teams
- Operations teams automate recurring documentation and slide generation
- Used for templated reports (weekly summaries, meeting recaps, incident writeups)
- Source: Company case studies; LinkedIn testimonials from enterprise customers
3. Research Consolidation
- Research teams aggregate findings across multiple papers without manual extraction
- Useful for literature reviews and synthesis tasks
- Source: User testimonials
Real Limitations
1. Latency Genspark's multi-agent orchestration causes significant delays:
- Simple queries: 15–30 seconds
- Complex research: 30–60 seconds
- Workflows with video/code generation: 2–5 minutes
For breaking news or real-time fact-checking, this is unusable. Google's <1-second response is non-negotiable for these use cases.
2. Data Freshness Genspark indexes pre-cached sources rather than crawling in real-time. Result: Breaking news appears 2–6 hours late. Live price feeds, weather data, and rapidly evolving documentation are unreliable.
For time-sensitive queries, users must supplement with real-time APIs.
3. Context Retention Genspark acknowledges context drift in extended sessions. After 30+ minutes or 10+ consecutive queries, the copilot occasionally loses thread continuity. Effects:
- Duplicate agent executions
- Loss of earlier refinement parameters
- Requiring users to re-state context
This limits reliability for long-running analytical sessions.
4. Accuracy and Hallucination Critical limitation: Genspark has not published hallucination rates or independent accuracy benchmarks.
From user reports on G2: "Occasionally generates plausible-sounding but false citations" and "Sometimes conflates information from multiple sources."
For high-stakes decisions (legal, medical, financial), human verification is mandatory.
5. Learning Curve Integrating custom agents or connecting specialized APIs requires:
- Understanding agent delegation patterns
- JSON configuration for API schemas
- Debugging multi-agent failures
This exceeds non-technical users' comfort level, limiting adoption in some enterprise settings.
6. Performance on Low-Spec Devices Sparkpages aggregating 50+ sources render slowly on older laptops or mobile devices. Official specifications not published.(See AI Music Generators 2025 for parallel tool evolution.)
Pricing and Business Model
Tier Structure
| Tier | Cost | Limits | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Free | $0 | 200 daily credits, GPT-5 access, core agents | Students, evaluators |
| Plus | $24.99/mo | Unlimited GPT-5 tokens, priority processing | Individual analysts |
| Pro | $249.99/mo | Multi-user seats, API automation, advanced media generation, dedicated support | Teams, small enterprises |
| Enterprise | Custom | Custom agents, security auditing, SLA guarantees | Large enterprises |
Business Model Analysis
Genspark's $50 million ARR with 88% paid retention suggests:
- Freemium funnel is working (free tier converts to paid)
- Enterprise deals contribute significantly to revenue
- Pricing ($25–250/month) targets productivity suites, not casual consumers
Compared to:
- Perplexity: $20/month, narrower focus (search-only)
- ChatGPT Plus: $20/month, broader appeal but less automation
- Genspark: Higher entry cost ($25–250) but broader automation coverage
The pricing reflects positioning: productivity layer for teams, not consumer search tool.

Genspark AI pricing page showing Free, Plus, Pro tiers
Technical Depth
Architecture Overview
Genspark uses a supervisor-agent pattern: one master agent coordinates sub-agents via standardized API calls. This differs from earlier systems like AutoGPT, which used direct LLM-to-LLM communication and suffered from hallucination compounding.
Benefits:
- Cleaner error handling (API calls are verifiable)
- Reduced hallucination propagation
- Easier to debug (execution is traceable)
Tradeoffs:
- Latency from inter-agent communication
- Complexity in handling agent disagreement
Known Technical Gaps
Genspark's documentation doesn't clarify:
- Which LLMs power it? The company mentions GPT-5 integration but doesn't confirm if it's the only backbone or one of many.
- How does conflict resolution work? When two agents produce contradictory outputs, what's the resolution mechanism? Voting? Confidence scoring? Unclear.
- What's the error rate? No published accuracy benchmarks exist.
- How does it scale? Performance at 10,000+ concurrent users is unknown.
Comparison to Competitors
vs. Claude with tool use: Claudecan achieve similar multi-step execution via APIs, but requires developer integration. Genspark is UI-driven. Claude has better reasoning on theoretical problems.
vs. ChatGPT Assistants: ChatGPT can also execute multi-step workflows via Assistants API. OpenAI could replicate Genspark's UI in weeks if prioritized. Genspark's advantage: it's already built.
vs. Zapier + GPT: Zapier is vastly more capable (1M+ apps) but requires workflow configuration. Genspark is simpler for non-developers. Zapier is more flexible for complex scenarios.
The reality: None of these are clearly "better." Each wins in different scenarios. Genspark wins on simplicity; competitors win on flexibility, accuracy, or scale.
FAQ
How does Genspark differ from ChatGPT + Zapier?
ChatGPT + Zapier requires manual workflow configuration (if-then logic, conditional routing, error handling). You need to set up each integration separately. Genspark abstracts this into natural language prompts. For non-developers, Genspark is easier. For complex scenarios requiring granular control, Zapier is more powerful.
Is Genspark suitable for mission-critical automation?
No. Context drift, occasional accuracy issues, and unverified hallucination rates make it unsuitable for high-stakes decisions (legal, medical, financial). For low-risk, repeatable tasks (report generation, documentation), yes. Human verification is mandatory for critical decisions.
How does phone call automation work?
Genspark integrates OpenAI's Realtime API to conduct voice conversations for simple tasks like scheduling appointments or confirming information. The feature is in beta; complex negotiations or customer service aren't supported.
What happens to my data?
Data processing occurs on Genspark's infrastructure. Full privacy terms are on the company website. Enterprise tiers may include data residency options, but this isn't publicly confirmed.
How long does a Sparkpage take to generate?
Simple queries: 15–30 seconds. Complex multi-source research: 30–60 seconds. Workflows with design or video: 2–5 minutes.
Can I export Sparkpages?
Yes. Formats include PDF, Markdown, CSV, and direct Notion database sync.
What's an open-source alternative?
LangChain, AutoGPT, and n8n offer open-source multi-agent frameworks. These require developer setup but provide full customization and data control.
Conclusion
Genspark represents a meaningful shift: from information retrieval to task execution. Its multi-agent architecture enables end-to-end automation that conventional search engines and chatbots don't natively support.
What Works
- Structured document generation from unstructured research
- Multi-step workflow automation without external tool configuration
- Native integrations with productivity platforms
- Strong business metrics ($50M ARR, 88% retention) indicating product-market fit
What Remains Uncertain
- Accuracy and hallucination rates (not independently verified)
- Scalability at enterprise volumes (not published)
- Long-term competitive sustainability (Google, OpenAI could replicate in 6 months)
- Context retention reliability for extended sessions
Who Should Use It
- Analysts and researchers automating recurring reports
- Operations teams standardizing documentation workflows
- Content teams accelerating asset production
- Anyone seeking to reduce context-switching between research, drafting, and publishing
Who Shouldn't
- Users needing real-time data (breaking news, live markets)
- High-stakes technical queries requiring peer-reviewed sources
- Teams requiring 99.9% uptime and accuracy
- Organizations requiring self-hosted infrastructure
The Bigger Picture
Genspark's commercial viability suggests autonomous agent frameworks are leaving research and entering production. Whether this becomes standard or remains niche will depend on how quickly competitors (Google, OpenAI, Anthropic) replicate similar functionality and whether the context drift and accuracy issues get solved.
For now, Genspark works best as a complement to existing tools, not a replacement.
Sources
- Reuters (June 2024) — Genspark raises $60M seed funding
- SiliconANGLE (February 2025) — Genspark $100M Series A at $530M valuation
- Forbes (October 2025) — Genspark in talks for $200M+ at $1B+ valuation
- Crunchbase — Genspark company profile
- OpenAI Platform Docs — Realtime API Guide
- Genspark.ai — Official documentation
- G2 Reviews — Genspark user reviews (50+ reviewers, October 2025)
- Capterra — Genspark user ratings and case studies
- The Age of Robotics (February 2025) — Genspark Series A analysis
- LinkedIn — Public testimonials from Genspark employees and enterprise customers
Methodology Note
This analysis synthesizes publicly available information from venture reports, media coverage, user reviews, and company documentation. No independent testing or product evaluation was performed. Prospective users should verify performance claims through free tier trials before committing to paid plans.
Why This Article Differs from Marketing
Unlike company marketing materials, this analysis:
- Acknowledges accuracy issues aren't verified
- Explains real limitations (latency, context drift, data freshness)
- Compares Genspark to actual alternatives (Claude, Zapier, ChatGPT) honestly
- Defines who shouldn't use the product
- Admits what isn't publicly known
This is analysis, not promotion.