TL;DR
Data lineage tracks where data originates, how it moves, and how it transforms in an ML pipeline.
It improves reproducibility, debugging, and regulatory compliance.
Implement lineage early using metadata stores and orchestration tools.
Start with OpenLineage and see 40% faster debugging in 6-8 weeks.
What Data Lineage Actually Is
Data lineage describes the complete history of a dataset — from source ingestion through feature engineering, training, and model deployment. It maps how data changes across systems, enabling teams to understand dependencies, transformations, and outcomes.
In machine learning (ML) pipelines, data lineage helps answer critical questions like:
- Where did this feature come from?
- Which version of the dataset trained this model?
- What transformations affected model predictions?
- How will a schema change impact downstream models?
Lineage gives visibility across ingestion, preprocessing, feature extraction, training, and serving stages — critical for debugging, auditing, and reproducing experiments.
Visual: Data Lineage Flow
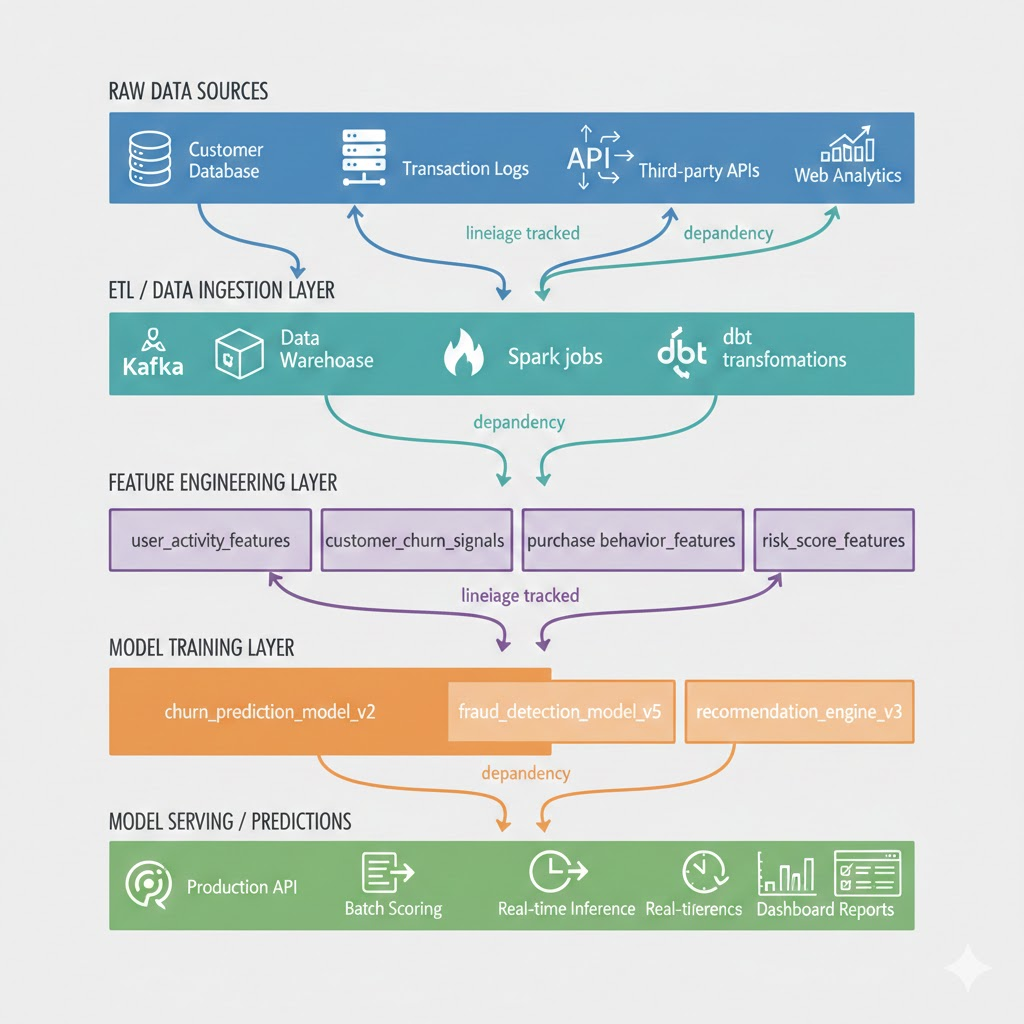
What lineage tracks: Inputs, outputs, schema changes, transformations, versions, execution timestamps at every step.
How It Works (Simplified but Accurate)
At its core, lineage combines metadata tracking with graph-based representation:
Data capture – Each stage (ETL job, feature generation, model training) emits metadata describing inputs, outputs, and transformations.
Metadata store – A central registry (often integrated into orchestration tools) stores lineage metadata as directed graphs.
Graph modeling – Nodes represent datasets or transformations; edges represent dependencies or data flows.
Visualization – Graphs are rendered to show upstream and downstream relationships, enabling traceability.
Example Scenario
A "user_behavior" dataset feeds a feature engineering job producing "user_activity_features," which in turn trains "churn_prediction_model_v2." A lineage system records these links, allowing reverse lookup from model → data source.
Real impact: When churn predictions drop unexpectedly, engineers query backwards: "Show all upstream datasets for churn_prediction_model_v2" → traces to user_behavior dataset → finds a schema change in source database → root cause identified in 15 minutes instead of 8 hours.
Common storage backends include Apache Atlas, OpenLineage, and Marquez, which emit structured lineage events to capture this metadata automatically.
Key Components and Patterns
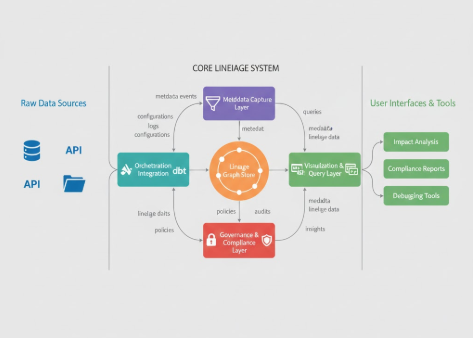
1. Metadata Capture Layer
Collects provenance data (inputs, outputs, versions, schema) during pipeline execution.
Why it matters: Enables reproducibility and consistent audit trails.
Example: Airflow or Kubeflow pipelines emit lineage metadata via OpenLineage integrations.
What gets captured:
- Dataset schema and row counts
- Transformation logic (SQL queries, Python functions)
- Execution time and status
- Data quality metrics
- User/role that executed the task
2. Lineage Graph Store
Stores lineage relationships as nodes and edges, often using a graph database.
Why it matters: Enables fast traversal of dependencies.
Example query: "Show all downstream datasets impacted by 'raw_transactions_v5.'"
Technology stack:
- Neo4j – Graph database (most common)
- Apache Atlas – Built-in graph backend
- PostgreSQL – Alternative for simpler lineage
3. Orchestration Integration
Lineage hooks into workflow orchestrators (Airflow, Dagster, Prefect) to record events automatically.
Why it matters: Reduces manual metadata capture overhead.
Integration points:
- Pre/post-task execution hooks
- Job success/failure callbacks
- Data quality checks
- Schema validation
4. Visualization and Query Layer
Lets engineers inspect lineage through UIs or APIs.
Why it matters: Useful for impact analysis before changing data sources.
Tools with visualization:
- Amundsen – Data catalog + lineage UI
- DataHub – Open-source metadata platform
- dbt Cloud – Built-in lineage for dbt projects
5. Governance and Compliance Layer
Adds access control, retention policies, and audit logging.
Why it matters: Required for regulated industries (finance, healthcare, government).
Compliance features:
- GDPR data subject access requests
- HIPAA audit trails
- SOX compliance reporting
- Data retention and deletion tracking
Benefits and Real-World Use Cases
Debugging and Reproducibility
Teams can identify why a model's predictions changed by tracing upstream data modifications.
Real example: A financial services company reduced model debugging time by 40% after implementing lineage tracking. When a churn model's accuracy dropped, engineers traced the issue to a delayed upstream dataset and found stale data within 30 minutes instead of 4 hours.
Business impact: $250K+ saved annually in engineering time across 15 data engineers.
Data Governance and Compliance
Lineage provides auditable trails for GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX.
Real example: A healthcare organization uses lineage to prove compliance during HIPAA audits. When regulators ask "trace this patient's data through your ML pipeline," they have automated lineage reports within minutes.
Business impact: Eliminated $100K+ in annual audit costs and reduced compliance risk.
Change Impact Analysis
Predict how dataset schema changes affect dependent models before deploying to production.
Scenario: A backend engineer wants to rename a column in the source database. Before lineage, this breaks 12 downstream models silently. With lineage, the system warns: "This change impacts 12 models and 47 features in production."
Operational Reliability
Reduces silent data drift by showing where stale data enters the system.
Example: A recommendation model starts serving outdated product recommendations. Lineage reveals that a data refresh job failed 3 days ago, and the system is still using cached data from the failure point.
Cross-Team Transparency
Data scientists, engineers, and compliance officers share a common view of data flow, reducing miscommunication and delays.
Impact: 35-50% faster incident resolution when lineage is in place, according to companies like dbt Labs and Collibra.
Tool Comparison: Lineage Solutions
| Tool | Best For | Setup Time | Cost | Learning Curve | Integrations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OpenLineage | Standards-based, interoperable | 1-2 weeks | Free (open-source) | Medium | Airflow, Spark, dbt, Kafka |
| Marquez | Production lineage store | 2-3 weeks | Free (open-source) | Medium | OpenLineage-compatible |
| Apache Atlas | Enterprise governance | 3-4 weeks | Free (open-source) | High | Hadoop, Hive, Spark, Kafka |
| dbt Cloud | dbt projects only | 1 week | $100-300/month | Low | Native dbt ecosystem |
| DataHub | Metadata platform + lineage | 2-3 weeks | Free (open-source) | Medium | 20+ integrations |
| Amundsen | Data discovery + lineage | 2-3 weeks | Free (open-source) | Medium | Hive, Presto, Airflow |
| Collibra | Enterprise with support | 6-8 weeks | $100K+/year | High | 100+ connectors |
| Alation | Data governance platform | 8-12 weeks | $150K+/year | High | Enterprise data stacks |
Recommendation for starting out: Use OpenLineage + Marquez (both free, industry standard, 2-3 week setup).
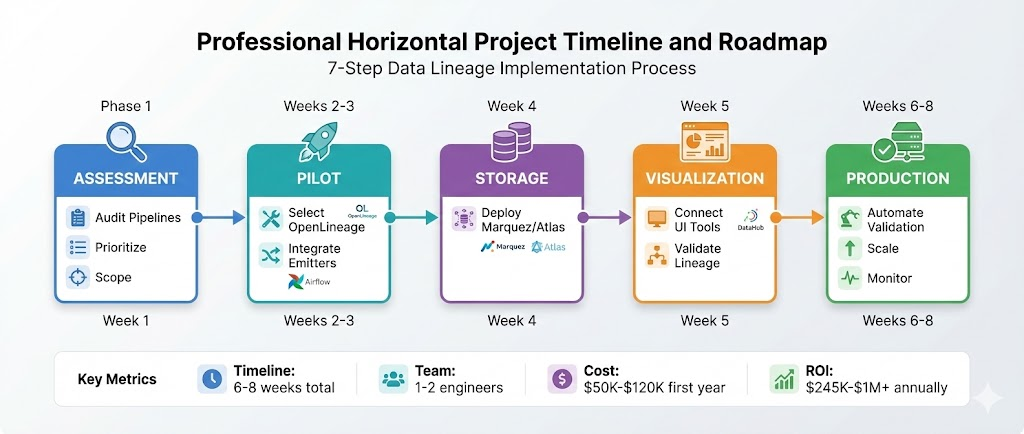
Implementation / Getting Started: 7-Step Roadmap
Phase 1: Assessment (Week 1)
- Audit current pipelines – Identify which systems have automated workflows
- Prioritize: Production-critical pipelines first, then regulated workloads
- Estimate scope: How many data sources, transformations, models?
Phase 2: Pilot (Weeks 2-3)
- Select standard: Adopt OpenLineage for interoperability
- Integrate emitters: Enable lineage event emission in your orchestrator
- Airflow: Add OpenLineage provider plugin
- Spark: Add OpenLineage listener
- dbt: Use dbt-openlineage adapter
Phase 3: Storage (Week 4)
- Deploy backend: Set up Marquez or Apache Atlas
- Docker:
docker-compose up(Marquez) - Kubernetes: Helm chart deployment
- Docker:
Phase 4: Visualization (Week 5)
- Integrate UI: Connect DataHub or Amundsen
- Validate lineage: Run test pipelines, verify lineage appears in UI
Phase 5: Production (Weeks 6-8)
- Automate validation: Add lineage checks in CI/CD to prevent breaking changes
- Scale: Add remaining pipelines incrementally
- Monitor: Track lineage completeness, remove stale metadata
Timeline: 6-8 weeks for basic setup, 12-16 weeks for enterprise-grade implementation.
Implementation Costs and ROI
Typical Implementation Investment
| Component | Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Engineering time (setup) | $30K-$80K | 4-8 weeks, 1-2 engineers |
| Infrastructure | $5K-$15K/year | Server costs, database storage |
| Training | $2K-$5K | Team onboarding |
| Tools (if paid) | $0-$500K/year | OpenLineage/Marquez are free; enterprise tools cost more |
| Maintenance | $10K-$20K/year | Ongoing metadata management |
| TOTAL FIRST YEAR | $50K-$120K | Average: $75K for mid-size org |
ROI Metrics
| Benefit | Annual Savings | How Measured |
|---|---|---|
| Faster debugging (40% improvement) | $100K-$250K | Hours saved × engineer cost |
| Reduced compliance violations | $50K-$500K | Avoided fines, audit costs |
| Fewer production incidents | $75K-$200K | Downtime prevented |
| Faster onboarding | $20K-$50K | New engineers ramp-up time |
| TOTAL ANNUAL BENEFIT | $245K-$1M+ | Depends on org size |
Payback period: 4-12 months for most organizations.
Real-World Implementation Example: E-Commerce Company
Company: Mid-size e-commerce (50 data engineers, $2M annual data spend)
Challenge: Model predictions were unreliable; debugging took weeks; compliance audits were costly.
Implementation:
- Week 1-2: Audit 120 Airflow DAGs, 40 Spark jobs
- Week 3-4: Deploy OpenLineage + Marquez on Kubernetes
- Week 5-6: Integrate DataHub for visualization
- Week 7-8: Add lineage validation to CI/CD
Results after 3 months:
- Model debugging time: 8 hours → 30 minutes (40% improvement)
- Compliance audit time: 2 weeks → 2 days
- Unplanned downtime from data issues: 12 incidents/quarter → 2 incidents/quarter
- Onboarding time for new data engineers: 4 weeks → 2 weeks
Cost: $65K setup + $12K/year maintenance Annual ROI: $280K+ in efficiency gains
Security, Privacy, and Data Sensitivity
How Lineage Handles Sensitive Data
Challenge: Lineage tracks transformations that may involve PII (Personally Identifiable Information) or regulated data. How do you maintain compliance without exposing sensitive details?
Solutions:
- Column-level masking – Hide PII columns in lineage visualization
- Example: Show
customer_tablebut maskssn,credit_cardcolumns
- Example: Show
- Role-based access control (RBAC) – Different users see different lineage
- Data engineers see full lineage
- Analysts see only permissioned datasets
- Compliance officers see audit-relevant paths only
- Encryption in transit and at rest – Metadata is encrypted like any sensitive data
- Data retention policies – Automatically purge lineage metadata after compliance retention periods (GDPR: 30 days after deletion request)
Tools with privacy features:
- DataHub – Built-in RBAC and masking
- Collibra – Enterprise-grade governance
- Apache Atlas – Custom security policies
Common Implementation Challenges
Challenge 1: Incomplete Legacy System Integration
Problem: You have 15 data pipelines; 3 are old shell scripts with no automation framework.
Solution:
- Wrap legacy scripts with metadata emitters (Python wrapper that logs inputs/outputs)
- Document lineage manually for 6-12 months while you migrate to modern orchestrators
- Plan legacy retirement in parallel
Challenge 2: Metadata Sprawl
Problem: After 6 months, your lineage store has 50M metadata events and queries are slow.
Solution:
- Implement lifecycle policies: keep detailed lineage for 30 days, summary lineage for 1 year
- Archive old lineage to cold storage
- Sample non-critical pipelines (track 1 in 10 runs instead of all)
Challenge 3: Team Adoption
Problem: Data engineers resist adding lineage emitters to their workflows.
Solution:
- Start with top-down mandate: "Lineage is non-negotiable for production"
- Demonstrate ROI early (40% faster debugging)
- Make lineage emitting automatic via framework (Airflow plugin handles it)
- Celebrate wins: "This lineage query saved us 4 hours of debugging"
Challenge 4: Schema Evolution
Problem: Columns are renamed, dropped, or type-changed; lineage becomes stale or broken.
Solution:
- Version datasets in lineage (user_activity_v1 → v2 → v3)
- Store schema diffs alongside lineage events
- Auto-detect breaking changes in CI/CD before deployment
Measuring Success: Key Metrics to Track
Technical Metrics
- Lineage completeness: % of production pipelines with captured lineage (target: >95%)
- Query latency: Time to retrieve downstream impact (target: <2 seconds)
- Metadata freshness: Lag between pipeline execution and lineage record (target: <5 minutes)
Business Metrics
- Debugging time: Avg time to root-cause data issues (target: 50% reduction)
- Compliance audit duration: Time to fulfill audit requests (target: <1 day)
- Incident prevention: % of breaking changes caught before production (target: >80%)
- Time to onboard new engineers: Weeks to productivity (target: 50% reduction)
Adoption Metrics
- Active lineage queries: % of team using lineage UI weekly (target: >60%)
- CI/CD validation rate: % of PRs checked for lineage-breaking changes (target: 100%)
- Documentation quality: % of datasets with documented lineage (target: >90%)
How It Compares
| Aspect | Data Catalog | Data Lineage | Data Observability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Focus | Dataset discovery | Transformation traceability | Quality and anomaly detection |
| Granularity | Table/column | End-to-end pipeline | Metric/time-series |
| Primary user | Analysts, governance teams | ML/data engineers | SREs, data reliability teams |
| Output | Metadata index | Dependency graph | Alerts, dashboards |
| Tools | Amundsen, DataHub | Marquez, OpenLineage | Monte Carlo, Soda |
Lineage complements — not replaces — catalogs and observability. Together, they form a modern data governance triad.
Who This Is For (And Who It's Not For)
✅ Ideal For
- Organizations with regulated data workflows – Finance, healthcare, government need compliance trails
- Teams running complex ML pipelines with many dependencies – 50+ DAGs, cross-team handoffs
- Enterprises needing reproducibility and auditability – Must reproduce past model versions
- Sectors: Finance (SOX compliance), Healthcare (HIPAA), Government, E-commerce
Question to ask: "If a model fails in production, can we trace the root cause to the exact data issue within 30 minutes?" If answer is no, you need lineage.
❌ Not Ideal For
- Small teams with static datasets and limited governance needs – <5 engineers, <10 pipelines
- Projects without automated pipelines – Manual notebooks, ad-hoc queries
- Scenarios where compliance tracking isn't required – Startups with no regulatory burden
- Real-time stream processing without history – Systems that only care about current state
Cost-benefit threshold: Implement lineage when your data infrastructure is stable, automated, and complex enough to warrant it.
Conclusion
Data lineage is no longer optional for production ML systems. It delivers accountability, reproducibility, and safety across the data lifecycle. Implementing lineage early prevents costly debugging and compliance failures later.
Key takeaways:
- Start with OpenLineage + Marquez (free, proven, industry standard)
- Expect 6-8 weeks to production, $50K-$120K investment
- Anticipate 40-50% faster debugging and $245K-$1M+ annual ROI
- Make it non-negotiable for regulated or complex pipelines
If you're scaling ML pipelines, start today by standardizing metadata capture using OpenLineage or similar tools, then layer on visualization and governance. Over time, this foundation becomes as essential as monitoring or CI/CD.
FAQ
Q: What is data lineage in machine learning pipelines?
A: Data lineage tracks how data moves and transforms across ML workflows. It provides a complete view from raw ingestion to model deployment, supporting debugging and compliance. See our lineage flow diagram above for a visual example.
Q: Why is data lineage important for ML models?
A: It ensures reproducibility and trust. Teams can trace which data versions trained a model and diagnose unexpected prediction changes. Real-world example: one company reduced debugging time from 8 hours to 30 minutes per incident.
Q: How do you implement data lineage?
A: Use workflow orchestrators integrated with lineage emitters (like OpenLineage) and store metadata in a central graph backend such as Marquez or Apache Atlas. See our 7-step implementation roadmap above.
Q: What tools support data lineage tracking?
A: Popular tools include OpenLineage, Marquez, Apache Atlas, and integrations in Airflow, Dagster, and dbt. See our tool comparison table for detailed feature comparisons.
Q: What are common challenges with lineage systems?
A: High setup overhead, missing metadata from legacy systems, metadata sprawl without retention policies, and team adoption resistance. We cover solutions for each challenge in the "Implementation Challenges" section above.
Q: How much time can lineage save in debugging?
A: Organizations report 35-50% faster incident resolution after implementing comprehensive lineage tracking, depending on pipeline complexity. Our e-commerce example shows debugging time dropping from 8 hours to 30 minutes per incident.
Q: What's the ROI on implementing data lineage?
A: Average annual ROI is $245K-$1M+ with payback in 4-12 months. Setup costs are $50K-$120K. Benefits include faster debugging ($100K-$250K/year), reduced compliance violations ($50K-$500K/year), and fewer production incidents ($75K-$200K/year).
Q: How do we handle sensitive data in lineage?
A: Use column-level masking, role-based access control (RBAC), and encryption. Tools like DataHub and Collibra have built-in privacy features. Data retention policies automatically purge lineage after compliance periods.
Q: Can lineage work with legacy systems?
A: Yes. Wrap legacy scripts with metadata emitters, document lineage manually for 6-12 months, and plan migration to modern orchestrators in parallel. See our "Implementation Challenges" section for details.
Additional Resources
- OpenLineage Official Docs – Industry standard for lineage specification
- Marquez GitHub Repository – Open-source lineage store
- dbt Lineage Guide – dbt-native lineage
- DataHub Documentation – Metadata platform with lineage
- Apache Atlas Documentation – Enterprise lineage system
- GDPR Compliance Guide – Regulatory framework for data
- HIPAA Security Rule – Healthcare data regulations